AI Impact on Labor Market: Insights from Recent Studies
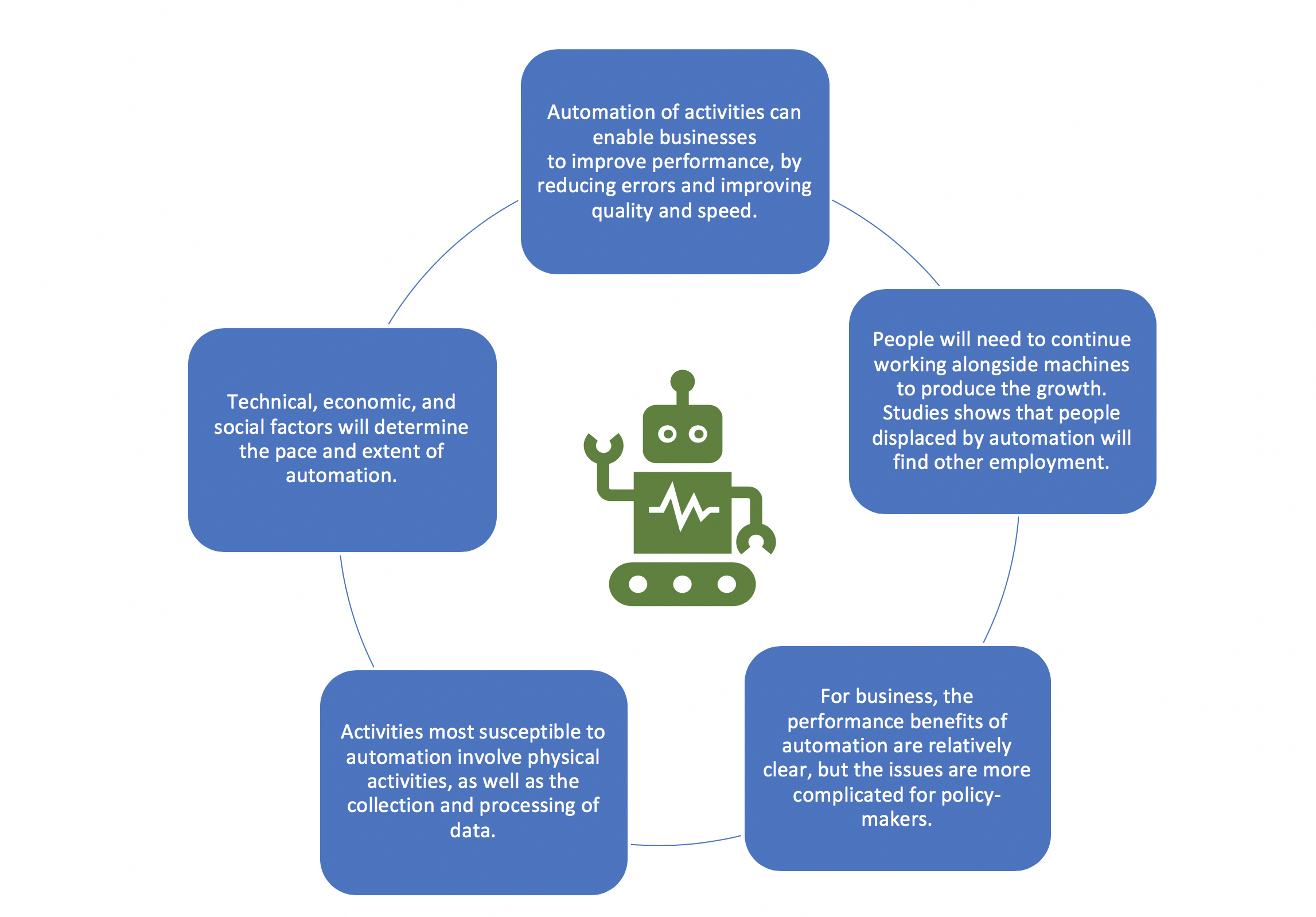
The impact of AI on the labor market is becoming increasingly evident as researchers highlight its role in reshaping employment landscapes. A recent study by economists at Harvard emphasizes how artificial intelligence is driving significant changes in workforce dynamics, leading to both opportunities and challenges for workers. As technological disruption influences jobs, understanding AI and employment trends is essential for navigating the future of work and AI. In particular, the notion of “occupational churn” reveals how various professions are experiencing volatility as new technologies emerge. This evolution requires adaptability from the workforce to keep pace with the rapid changes brought about by automation and AI advancements.
The influence of intelligent technologies on labor dynamics is a topic gaining considerable attention in today’s economy. Insights from Harvard economists shed light on how advancements in automation and artificial intelligence are not only revitalizing employment structures but also presenting new challenges for various sectors. As we analyze the future of work along with these technological disruptions, it becomes clear that understanding workforce shifts is crucial for both employers and employees alike. The term “workforce transformation” encapsulates the changes brought on by these developments, signifying a need for adaptation in skills and job roles across industries. Therefore, comprehending the implications of AI on our professional landscape is critical for preparing for the forthcoming shifts in the job market.
The Role of AI in Shaping the Labor Market
The rise of artificial intelligence is increasingly shaping the dynamics of the U.S. labor market, as evidenced by recent trends outlined by researchers Deming and Summers. A pivotal aspect of their findings is how AI contributes to shifts in job distribution across various sectors. This transformation reflects not only technological adaptation but also the changing needs for skills within the workforce. With AI driving efficiency, jobs that require unique human skills or creativity are emphasized, pointing towards a future where human workers may co-exist with machines in increasingly specialized roles.
AI’s role is not merely to replace but to redefine job functions. For instance, as companies integrate AI into their workflows, there is a discernible shift from rote tasks to positions that necessitate critical thinking and emotional intelligence. As the landscape evolves, future employees must adapt to these new expectations, emphasizing continuous learning and upskilling to align with AI-driven job requirements.
Technological Disruption and Job Trends
Technological disruption, particularly through AI, has contributed significantly to changing job trends over the last century. The term ‘job polarization’ describes how employment is increasingly concentrated at both ends of the wage spectrum, with a noticeable decline in middle-income positions. As noted in the study by Deming and Summers, the resurgence of high-paid roles for specialized skill sets indicates that while AI may eliminate certain jobs, it also fosters the creation of new ones that demand advanced competencies in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM).
These job trends highlight an ongoing necessity for adaptation within the labor market. While there is a rise in demand for tech-savvy professionals, many occupations in low-wage service sectors are witnessing stagnation or decline. This dynamic underscores the complexities of technological disruption, where the creation of jobs often occurs alongside significant occupational churn, leaving many workers facing the challenge of navigating this rapidly evolving employment landscape.
Occupational Churn and Its Impacts
Occupational churn, the rate at which consumers change occupations, provides vital insights into the effects of technological change on the labor market. Data from the last century indicate a historical context to these shifts, and the recent findings suggest a significant shift towards instability bolstered by AI advancement. The uptick in occupational churn since 2019 points to a labor market in flux, raising concerns regarding job security and the need for adaptable skills.
As AI continues to integrate into various industries, the potential for disruption can be both daunting and exciting. Workers must confront the reality that their roles may evolve or be supplanted by automation. Consequently, this necessitates a proactive approach in career development, where individuals seek to enhance their skills continuously to stay relevant in a landscape marked by rapid technological shifts.
AI and Employment Trends: Future Implications
The researchers identified critical AI and employment trends that could shape the future of work. With increasing investments in AI technologies, the trend points toward a growing demand for specialized skills while simultaneously diminishing opportunities in traditional roles. This indicates a fundamental shift in how jobs are created and what skills are deemed valuable, compelling workers to embrace new learning pathways to secure their place within the modern economy.
As AI solutions become more entrenched across sectors, the implications for employment models are profound. Organizations may prioritize hiring skilled individuals who can seamlessly integrate technology into their work processes rather than training workers with basic skills. This emphasis on proficiency in emerging technologies will likely augment competitive pressure among job seekers, advocating for a workforce that is educated, adaptable, and ready to engage with a technology-driven future.
The Future of Work and AI: Challenges Ahead
Navigating the future of work involves acknowledging the dual impact of AI: enhancing productivity while presenting challenges for workforce stability. The historical patterns of occupational churn reveal that certain sectors may diminish, while others expand, suggesting a reallocation of labor rather than a total displacement. Industries must prepare for these shifts by recognizing that investing in human capital is crucial for sustaining growth amid technological disruptions.
Moreover, employers face increased expectations from a workforce that is now aware of how AI can enhance efficiency. As highlighted by Deming, the pressure to deliver rapid results will heighten, pushing employees and employers alike to adopt a mindset geared towards collaboration with AI technologies. The future will not solely be about performing traditional tasks but rather redefining roles to embrace innovation.
Adapting to the Changing Landscape of Employment
The landscape of employment is undergoing profound changes due to the rise of AI-driven technologies. As traditional roles are redefined, it is imperative for both workers and organizations to adapt effectively. Employees must cultivate a mentality of lifelong learning, continually updating their skills to align with emerging job demands. This transition underscores the importance of upskilling programs and educational initiatives that focus on equipping workers with the tools necessary to thrive in an AI-augmented workspace.
Organizations also have a role to play in facilitating this transition by creating an environment that encourages continuous professional development. This may include offering training programs or establishing mentorship opportunities to help employees navigate the complexities of new technologies. By fostering a culture that embraces change and innovation, companies can not only retain their workforce but also position themselves advantageously in an ever-evolving labor market.
The Economic Role of AI in Job Creation
As AI technologies mature, their role in job creation becomes increasingly pronounced. Instead of solely displacing workers, AI is acting as a catalyst for the creation of new job categories that demand advanced skills and technical expertise. The increase in STEM job opportunities reflects a broader trend within the tech-driven economy, where innovation leads to new roles that did not previously exist, effectively reshaping the labor market.
Moreover, companies that invest in AI solutions often realize the potential for significant competitive advantages, requiring them to recruit top talent capable of leveraging these technologies effectively. This necessity for skilled workers not only drives demand in tech sectors but also has ripple effects across the economy as industries evolve in response to technological advancements, ultimately creating a more diverse job market.
Understanding Automation Anxiety and Its Effects
Automation anxiety has become a prevalent concern as workers express fears surrounding job security in the face of AI advancements. The notion that AI will replace human labor is rooted in historical narratives of technological disruption; however, the reality is more nuanced. While AI may automate certain tasks, it concurrently opens avenues for new roles that require human oversight, creativity, and emotional intelligence.
Research underscores that rather than eradicating jobs, AI fuels an evolution in workforce requirements, demanding adaptability and higher skill levels. Addressing automation anxiety necessitates transparent communication from employers about the implications of AI on current job functions and potential changes to workflows, setting the stage for a collaborative relationship between humans and machines.
Navigating the Future of Employment with AI
As we venture into an era increasingly influenced by AI, navigating the future of employment will require a strategic approach from both employees and employers. Workers must proactively seek ways to enhance their skills, focusing on areas where human capability intersects with AI technology. Those who can adapt to technological change will likely find themselves at an advantage in a labor market defined by the need for specialized skills.
Employers, on the other hand, need to recognize the importance of investing in human talent alongside technological innovations. By fostering a workspace that champions adaptability and training, organizations not only prepare their workforce for future challenges but also drive the overall success of their business in an AI-enabled economy.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is AI impacting the labor market today?
AI is significantly disrupting the labor market by changing job distributions and creating new employment trends. Recent studies show that while there was stability between 1990 and 2017, AI has led to increased occupational churn, indicating shifts in job types and industries, particularly favoring high-paid jobs for skilled workers.
What does occupational churn mean in relation to the artificial intelligence workforce?
Occupational churn refers to the rate at which jobs change in the labor market. In the context of the artificial intelligence workforce, it highlights how AI technologies are driving changes across various sectors, resulting in a significant transformation of job roles, especially towards more technical positions.
What are the trends in AI and employment as identified by recent research?
Recent research identified four key trends related to AI and employment: a decline in job polarization, an increase in STEM job shares, a drop in low-paying service jobs, and a significant decline in retail sales jobs. These trends indicate that AI is reshaping the labor market dynamics, creating opportunities primarily for high-skilled workers.
How does AI contribute to technological disruption jobs?
AI contributes to technological disruption jobs by automating tasks traditionally performed by humans and transforming job requirements, hence changing employment landscapes. Jobs that are routine or low-skilled are particularly vulnerable to displacement, while demand for highly skilled jobs in technology and AI-related fields is on the rise.
What is the future of work and AI in terms of job stability?
The future of work in the age of AI suggests reduced job stability for certain sectors, especially low-paying service roles, while simultaneously creating more opportunities in high-skilled areas like technology and data analysis. Workers will need to adapt to these changes as AI continues to evolve and influence job markets.
Are there any occupations particularly at risk due to AI adoption?
Yes, occupations particularly at risk due to AI adoption include low-paying service jobs, such as retail sales positions and certain administrative roles. The shift towards automation and predictive AI in sectors like e-commerce indicates that many of these jobs may not return, leading to long-term structural changes in the labor market.
What implications does the rise of AI have for future job seekers?
Job seekers in the future will likely need to prioritize skills in technology and artificial intelligence to remain competitive. The demand for STEM-related roles is increasing, and individuals will need to be adaptable and skilled in using AI tools to thrive in a changing job market.
How does AI influence knowledge workers and their responsibilities?
AI influences knowledge workers by raising expectations for productivity and efficiency. As organizations adopt AI capabilities, knowledge workers may face pressure to deliver higher-quality work in shorter timeframes, emphasizing the need to leverage AI tools effectively.
What measures can be taken to address the impact of AI on employment trends?
To address the impact of AI on employment trends, it’s essential to invest in education and training programs that equip workers with relevant skills, promote lifelong learning, and foster adaptability in the workforce. Policies supporting job transitions and creating safety nets for displaced workers will also be crucial.
Will AI replace all jobs in the labor market?
While AI is expected to automate certain tasks and roles, it is unlikely to replace all jobs. Instead, it will transform job functions and create new opportunities, particularly in areas requiring human creativity, critical thinking, and interpersonal skills. Adaptation and reskilling will be vital for workers.
| Trend | Key Findings |
|---|---|
| Job Polarization | Shift away from job polarization, favoring high-paid, skilled workers since the late 2010s. |
| STEM Job Growth | Increase in STEM jobs from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% in 2024, alongside significant investments in AI. |
| Decline in Low-Paying Jobs | Flat or declining employment in low-paying service jobs since 2019, factors include AI, wages, and market dynamics. |
| Reduction in Retail Jobs | Retail sales jobs dropped from 7.5% to 5.7% from 2013 to 2023, accelerated by AI and e-commerce growth. |
Summary
The AI impact on the labor market is significant and multifaceted, as highlighted by recent research that reveals shifts in job distribution and skill requirements. While the fear of widespread job displacement has caused anxiety, the findings show a complex picture where AI is driving growth in high-skilled sectors while simultaneously challenging traditional low-wage roles. As the landscape of employment continues to evolve, stakeholders must adapt to these changes and prepare for a future where AI plays a central role in the economy.